How Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) Works
Followed by azker‘s article on OSI model Part-1 and Part-2. In this article I will explain what this ARP and why it’s important to know about it. In OSI Layers you see there are two types of addresses in OSI model. Network layer contains IP address and Datalink layer contains MAC address. When I was learning OSI Layers this question came to me “Isn’t one address enough to communicate between devices?”.
Why we need two address types?
To make life easier, let’s take a look at a real life example. I want to meet my friend named Jim, But I don’t know exactly where he is now. Then I come outside and shout “Hey Jim where are you? :/”. Everybody in the area gets my message. Jim also hears that and responding me with his physical location, “Hey dude I’m here!”. Now I know his place and moving.
[lbfenix img=”http://i1134.photobucket.com/albums/m608/irfadraz/arp/Jim.jpg”]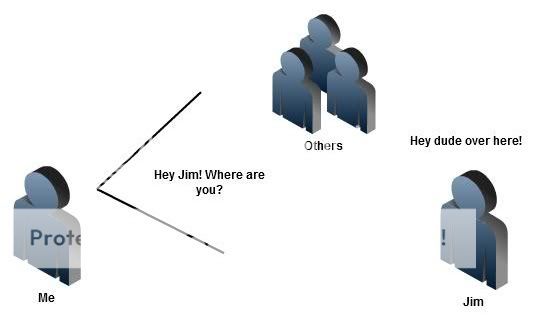 [/lbfenix]
[/lbfenix]
How we can relate it with Networking?
In above situation I already know my friend’s name, but I din’t know where he is right? I found his place by his response to my shout. This is exactly how network devices works. Let’s say I begin to transfer some data from my desktop with IP address 192.168.1.15 and need to my server with IP address 192.168.1.100. I tell my desktop to connect to the server by manually submitting server’s IP address. But my Desktop doesn’t know where exactly the server is. And Desktop will send a shout to the network know as ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) “Who is this 192.168.1.100?”. Every devices in the network get the message as it’s a broadcast packet. When server gets it, it’ll respond to the ARP request by giving server’s MAC (Media Access Control) address of the network adapter, which is the physical address of the server. And Desktop start sending data directly to server’s MAC address. And Desktop will keep servers MAC address in it’s arp cache. To view ARP cache entries, go to Start –> Run –> CMD and type arp -A
[lbfenix img=”http://i1134.photobucket.com/albums/m608/irfadraz/arp/ARP.jpg”]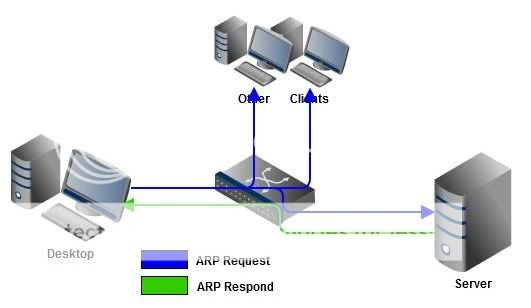 [/lbfenix]
[/lbfenix]
So now we know Network devices never communicate directly to a IP address. IP (A logical name) address is used to find it’s MAC (Physical) address with ARP.
What information is included in ARP packet?
Up to now we looked at how ARP works and used to find MAC by IP address. Now we’ll take a look at contents of the ARP packet.
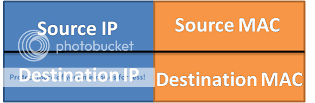
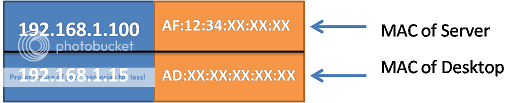
Basically ARP contents two addresses as illustrated below.
When Desktop sends ARP, it’ll look like this.
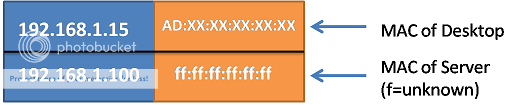
When Server responds to ARP request from Desktop it’ll look like this.
I hope this helped you to understand the basics of ARP functions. Wondering what can I do with ARP? It’s hacking time 😉

But Razik, When i’m learning the CCNA i learned the OSI Model of 7 logical layers, Right but ARP is a simply called as broadcast, How ARP Would work on a Router because routers default breakdown broadcasts, So How to send a broadcast message to a each person without sending to all hosts in a network segments, There are any way?
Sorry for the late reply xD. As ARP is a broadcast you can’t use it anyway like uni-cast and multicast. Routers basically eliminates broadcast, so hosts will learn the MAC of the router as gateway.
We are a bunch of volunteers and starting a brand new scheme in our community.
Your website offered us with helpful info to work on.
You have done a formidable task and our whole group
will probably be grateful to you.